Thursday, October 9, 2008
Auto Tachometer
Here is the circuit diagram for a Simple Auto Tachometer which can be used for any vechile. I tested this in my car and it works fine. My next plan is to replace the analoge meter with seven segment display unit. I'll upload it once I done. Please let me know if you find any technical issue with this circuit.
Wednesday, September 24, 2008
Find Solenoids

Vast requests about the 12V solenoids. Most of them have mentioned that they cannot find solenoids which are fitting for door security system. You can upload the blog regarding any problems occur with this. I’ll reply within two days time.
These solenoids are mostly available in motor spare part shops.
Thursday, September 18, 2008
Home Security - Implement Code Lock to a Home Door

The previous circuit (Digital Code Lock) can be easily applied to a home door or a window by using a solenoid.
For that you require 12 volts / 2 pin solenoid. Simply connect the two terminals of the solenoid to the A and B terminals of the circuit.
If you really interested, you can implement so many useful applications by using this circuit.
Wednesday, September 17, 2008
Extra Protection to your car
Implementing Digital Code Lock to Vehicles (Fig. 010A)
Key Pad (Fig. 010C)

9- digit key pads are mostly available in the market and very cheap in price. No worries, if anyone cannot find it, you can make one on your own. You just need 9 touch switches and a small Vero board.
Mount the Keypad in your car’s dash board nicely. Add an extra value to your vehicle by installing this unit. Connect A abd B terminals of Fig. 010A and Fig. 010B. Set the 12V supply to the circuit by the car battery.
You will get an extra protection to your can and no one can steal without knowing your 4 – digit security code.
If you have any doubt, please fell free to contact me via ciscocelincomf@gmail.com or post your comments to the blog.
I have so many ideas about customize security systems that can be built on your own and at very law cost.
This is a very important circuit for your vehicle. You can couple this circuit to the starter switch (Fig. 010B). Then the 4 - digit secrete code will be needed to start the vehicle. The code can be decided by you. You can change the code at any time with zero cost. Once you enter the code correctly only the starter path completes. (Ignition on)
Key Pad (Fig. 010C)

9- digit key pads are mostly available in the market and very cheap in price. No worries, if anyone cannot find it, you can make one on your own. You just need 9 touch switches and a small Vero board.
Mount the Keypad in your car’s dash board nicely. Add an extra value to your vehicle by installing this unit. Connect A abd B terminals of Fig. 010A and Fig. 010B. Set the 12V supply to the circuit by the car battery.
You will get an extra protection to your can and no one can steal without knowing your 4 – digit security code.
If you have any doubt, please fell free to contact me via ciscocelincomf@gmail.com or post your comments to the blog.
I have so many ideas about customize security systems that can be built on your own and at very law cost.
Sunday, September 14, 2008
Digital Code Lock for Home and Office Security


The Keypad must be the kind with a common terminal and a separate connection for each key. On a 12-key pad, look for 13 terminals. The matrix type with 7 terminals will NOT do. The Alarm is set by pressing a single key. Choose the key you want to use and wire it to 'E'. Choose the four keys you want to use to switch the alarm off, and connect them to 'A B C & D'. Your code can include the non-numeric symbols. With a 12-key pad, over 10 000 different codes are available. Wire the common to R1 and all the remaining keys to 'F'. When 'E' is pressed, current through D2 and R9 switches Q5 on. The relay energises, and then holds itself on by providing base current for Q5 through R10. The 12-volt output is switched from the "off " to the "set " terminal, and the LED lights. To switch the Alarm off again it is necessary to press A, B, C & D in the right order. The IC is a quad 2-input AND gate, a Cmos 4081. These gates only produce a high output when both inputs are high. Pin 1 is held high by R5. This 'enables' gate 1, so that when 'A' is pressed, the output at pin 3 will go high. This output does two jobs. It locks itself high using R2 and it enables gate 2 by taking pin 5 high. The remaining gates operate in the same way, each locking itself on through a resistor and enabling its successor. If the correct code is entered, pin 10 will switch Q4 on and so connect the base of Q5 to ground. This causes Q5 to switch off and the relay to drop out. Any keys not wired to 'A B C D or E' are connected to the base of Q3 by R7. Whenever one of these 'wrong' keys is pressed, Q3 takes pin 1 low. This removes the 'enable' from gate 1, and the code entry process fails. If 'C' or 'D' is pressed out of sequence, Q1 or Q2 will also take pin 1 low, with the same result. You can change the code by altering the keypad connections. If you need a more secure code use a bigger keypad with more 'wrong' keys wired to 'F'. A 16-key pad gives over 40 000 different codes. All components are shown lying flat on the board; but some are actually mounted upright. The links are bare copper wires on the component side. Two of the links must be fitted before the IC.
Home and Office Security - Useful Schematic Part A
This is a very useful circuit for home and office use. You can build this on your own. This is low cost and very high efficiency complete circuit which you can have. Try this. I'll help you on every step.

Description
This circuit features automatic Exit and Entry delays and a timed Bell Cut-off. It has provision for both normally-closed and normally-open contacts, and a 24-hour Personal Attack/Tamper zone. It is connected permanently to the 12-volt supply and its operation is "enabled" by opening SW1. By using the expansion modules, you can add as many zones as you require; some or all of which may be the inertia (shock) sensor type. All the green LEDs should be lighting before you open SW1. You then have up to about a minute to leave the building. As you do so, the Buzzer will sound. It should stop sounding when you shut the door behind you. This indicates that the Exit/Entry loop has been successfully restored within the time allowed. When you re-enter the building you have up to about a minute to move SW1 to the off position. If SW1 is not switched off in time, the relay will energize and sound the main bell. It will ring for up to about 40 minutes. But it can be turned off at any time by SW1. The "Instant" zone has no Entry Delay. If you don't want to use N/O switches, leave out R8, C8 and Q2; and fit a link between Led 3 and C7. The 24 Hour PA/Tamper protections are provided by the SCR/Thyristor. If any of the switches in the N/C loop is opened, R11 will trigger the SCR and the bell will ring. In this case the bell has no time limit. Once the loop is closed again, the SCR may be reset by pressing SW2 and temporarily interrupting the current flow. The basic circuit will be satisfactory in many situations. However, it's much easier to find a fault when the alarm is divided into zones and the control panel can remember which zone has caused the activation. The expansion modules are designed to do this. Although they will work with the existing instant zone, they are intended to replace it. When a zone is activated, its red LED will light and remain lit until the reset button is pressed. All the modules can share a single reset button.

Description
This circuit features automatic Exit and Entry delays and a timed Bell Cut-off. It has provision for both normally-closed and normally-open contacts, and a 24-hour Personal Attack/Tamper zone. It is connected permanently to the 12-volt supply and its operation is "enabled" by opening SW1. By using the expansion modules, you can add as many zones as you require; some or all of which may be the inertia (shock) sensor type. All the green LEDs should be lighting before you open SW1. You then have up to about a minute to leave the building. As you do so, the Buzzer will sound. It should stop sounding when you shut the door behind you. This indicates that the Exit/Entry loop has been successfully restored within the time allowed. When you re-enter the building you have up to about a minute to move SW1 to the off position. If SW1 is not switched off in time, the relay will energize and sound the main bell. It will ring for up to about 40 minutes. But it can be turned off at any time by SW1. The "Instant" zone has no Entry Delay. If you don't want to use N/O switches, leave out R8, C8 and Q2; and fit a link between Led 3 and C7. The 24 Hour PA/Tamper protections are provided by the SCR/Thyristor. If any of the switches in the N/C loop is opened, R11 will trigger the SCR and the bell will ring. In this case the bell has no time limit. Once the loop is closed again, the SCR may be reset by pressing SW2 and temporarily interrupting the current flow. The basic circuit will be satisfactory in many situations. However, it's much easier to find a fault when the alarm is divided into zones and the control panel can remember which zone has caused the activation. The expansion modules are designed to do this. Although they will work with the existing instant zone, they are intended to replace it. When a zone is activated, its red LED will light and remain lit until the reset button is pressed. All the modules can share a single reset button.
Wednesday, September 3, 2008
Car anti theft wireless alarm


This FM radio-controlled anti- theft alarm can be used with any vehicle having 6- to 12-volt DC supply system. The mini VHF, FM transmitter is fitted in the vehicle at night when it is parked in the car porch or car park. The receiver unit with CXA1019, a single IC-based FM radio module, which is freely available in the market at reasonable rate, is kept inside. Receiver is tuned to the transmitter's frequency. When the transmitter is on and the signals are being received by FM radio receiver, no hissing noise is available at the output of receiver. Thus transistor T2 (BC548) does not conduct. This results in the relay driver transistor T3 getting its forward base bias via 10k resistor R5 and the relay gets energized. When an intruder tries to drive the car and takes it a few meters away from the car porch, the radio link between the car (transmitter) and alarm (receiver) is broken. As a result FM radio module gene-rates hissing noise. Hissing AC signals are coupled to relay switching circuit via audio transformer. These AC signals are rectified and filtered by diode D1 and capacitor C8, and the resulting positive DC voltage provides a forward bias to transistor T2. Thus transistor T2 conducts, and it pulls the base of relay driver transistor T3 to ground level. The relay thus gets de-activated and the alarm connected via N/C contacts of relay is switched on. If, by chance, the intruder finds out about the wireless alarm and disconnects the transmitter from battery, still remote alarm remains activated because in the absence of signal, the receiver continues to produce hissing noise at its output. So the burglar alarm is fool-proof and highly reliable.
Friday, June 27, 2008
Cut Down Price
Due to many e-mail requests, I decided to implement this IR security system circuit with all the features such as alarm, relay activated switch/light, timer, regulated power unit and error correction circuit on a single PCB.
I can provide the PBC along with all the devices for a reasonable price. Interested parties, blog me. Please note that I’ll not reply for the email requests anymore starting from today.
I can provide the PBC along with all the devices for a reasonable price. Interested parties, blog me. Please note that I’ll not reply for the email requests anymore starting from today.
Thursday, June 12, 2008
My First Activity

Fig.017a shows mounting arrangement for both the transmitter and receiver units on the gate pillars. To achieve a high directivity of the IR beam towards the sensor, use a reflector behind the IR LED.
After both the units have been built, connect 6V power supply to the transmitter and the receiver circuits.
The transmitter and receiver units are aligned such that the IR beam falls directly on the IR sensor. As long as IR beam falls on the sensor, its output remains low.
When anyone interrupts the IR beam falling on the sensor, its output goes high to drive transistor into conduction and pin 2 of NE555 goes low momentarily. As a result, NE555 gets triggered and its pin 3 goes high to drive the relay circuit. Output pin 3 of NE555 remains high for around 30 seconds.
After both the units have been built, connect 6V power supply to the transmitter and the receiver circuits.
The transmitter and receiver units are aligned such that the IR beam falls directly on the IR sensor. As long as IR beam falls on the sensor, its output remains low.
When anyone interrupts the IR beam falling on the sensor, its output goes high to drive transistor into conduction and pin 2 of NE555 goes low momentarily. As a result, NE555 gets triggered and its pin 3 goes high to drive the relay circuit. Output pin 3 of NE555 remains high for around 30 seconds.
Tuesday, June 10, 2008
Connecting a Relay
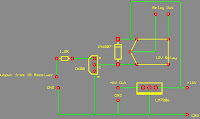
Here is the circuit diagram to connect a relay to the IR receiver end. Connect IR receiver's output to the 1.8K resistor. Use LM7806 regulator IC to get 6V for the IR transmitter and the receiver. You can connect any electronic/electrical appliance to the relay output and it works according to the receiver's output.
Wednesday, May 28, 2008
Saturday, May 24, 2008
IR Receiver Circuit Diagram
Below is the receiver circuit diagram. It comprises IR sensor TSOP1738 (IR RX1), npn transistor BC548, timer NE555 and some resistors and capacitors. IC is wired as a monostable multivibrator with a time period of around 30 seconds. You can control the output duration (currently ~30 Sec) by changing the value of the 47uf capacitor.


Tuesday, May 13, 2008
Free Tool for Design PCB's
Thursday, May 8, 2008
Build IR Transmitter Circuit (Fig. 1)
The astable multivibrator (NE555) oscillates at a frequency of around 38 kHz, which is transmitted by the IR LED. 47 Ohms resistor limits the current across the IR LED. The variable resistor (100K) is a must for the below circuit as we need to adjust the frequency of the transmitting IR signal.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)